Today, IT infrastructures are more and more complex and dynamic. With cloud infrastructure and applications based on containers, infrastructure changes quickly and must be up to date into your monitoring system.
The best way to be up to date is to use automatization with a configuration management tool. In this article we will be use Salt like configuration manager but methodology are the same for other tools.
Goals
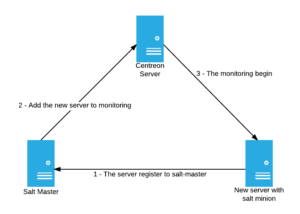
When a salt-minion is registered to the salt-master, the server with the salt-minion will be automatically added to the Centreon Web configuration with correct host templates. Then the poller will be reloaded.
Figure of the infrastructure to monitor
Prerequire
For this tutorial, you must have a good knowledge of host template and host group on Centreon Web.
The software requirement:
- SaltStack
- Centreon Web => of 2.8.x
- python-sdk-centreonapi => 0.0.1
Prepare your Centreon Web
You must have configured some hosttemplates and host groups.
For this tutotial, I will use the next host templates and hostgroups.
Host templates from Plugin Packs :
- Linux SNMP (operatingsystems-linux-snmp) : The base for monitor a linux server by SNMP
- Apache Server (applications-webservers-apache-serverstatus) : Monitor a http Apache server
- MySQL DB (applications-databases-mysql) : Monitor a MySQL server
Host groups:
- linux-servers : The list of linux servers
- frontend : The list of http servers
- backend : The list of database servers
Configure the salt-master
Add Centreon Web information into salt-master configuration
I suggest to use an additionnial file for this configuration like /etc/salt/master.d/centreon.conf.
The configuration keys:
| Key name | Description |
|---|---|
| url | The url to access to Centreon Web. |
| username | An user who can use the rest API |
| password | The password of this user. |
| poller | The poller where the new hosts will be monitored. |
| hosttemplates | The list of host templates for the new hosts. This list will be completed by minion configuration. |
| hostgroups | The list of host groups to attach the new hosts. This list will be completed by minion configuration. |
Example:
centreon:
url: http://centreon.domain.tld/centreon
username: username
password: password
poller: Central
hosttemplates:
- operatingsystems-linux-snmp
hostgroups:
- linux-servers
Write the salt-runner
The salt-runner will be runned on the salt-master. It calls the Centreon Web Rest API to register the new salt-minion. It been written in Python. See salt documentation for more information.
I uses the /srv/runners path for my runner programs. This path must be configured in /etc/salt/master, added at the end of file :
runner_dirs: ['/srv/runners']
Then I create the /srv/runners/centreon.py file which contains the code to add an host
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from __future__ import absolute_import
import json
import logging
import salt.client
# Import from python-sdk-centreonapi
from centreonapi.webservice import Webservice
from centreonapi.webservice.configuration.host import Host
from centreonapi.webservice.configuration.poller import Poller
# Initialize the default logger to write in salt-master log file
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# Create a class to interact with object
class Centreon(object):
def __init__(self):
# Get configuration
self.config = Centreon.getConfig()
# Initialize the webservice connector
Webservice.getInstance(
self.config['url'],
self.config['username'],
self.config['password']
)
# Initialize Centreon objects
self.host = Host()
self.poller = Poller()
# Initialize local salt client
self.salt_client = salt.client.LocalClient()
# Cache for salt grains
self.grans_cache = None
# Get the configuration from salt-master configuration file
@staticmethod
def getConfig():
centreon_config = __opts__['centreon'] if 'centreon' in __opts__ else None
if centreon_config is None:
raise KeyError('Not configuration found')
# Test required configuration parameters
url = centreon_config.get('url', None)
username = centreon_config.get('username', None)
password = centreon_config.get('password', None)
poller = centreon_config.get('poller', None)
if url is None or username is None or password is None or poller is None:
KeyError('Missing parameters')
hosttemplates = centreon_config.get('hosttemplates', [])
hostgroups = centreon_config.get('hostgroups', [])
if len(hostgroups) == 0 or len(hosttemplates) == 0:
KeyError('Missing parameters')
return {
'url': url,
'username': username,
'password': password,
'poller': poller,
'hosttemplates': hosttemplates,
'hostgroups': hostgroups
}
# Test if the host exists in Centreon Web configuration
def exists(self, minion_name):
try:
hosts = self.host.list()
except Exception as exc:
logger.error(exc)
raise exc
for info in hosts['result']:
if info['name'] == minion_name:
return True
return False
# Get the host ip address (use the first time when the host have multiple ip address)
def get_minion_ip(self, minion_name):
ip = self.salt_client.cmd(minion_name, 'network.ip_addrs')
if minion_name not in ip or len(ip[minion_name]) == 0:
raise KeyError('The minion has not ip !!! ...')
return ip[minion_name][0]
# Cache the grains centreon of the host to add
def get_grains_centreon(self, minion_name):
grains = self.salt_client.cmd(minion_name, 'grains.item', ['centreon'])
if minion_name not in grains:
self.grains_cache = {}
self.grains_cache = grains[minion_name]['centreon']
logger.error(json.dumps(self.grains_cache))
# Generate the list of hostgroups for the host to add
def get_hostgroups(self, minion_name):
if self.grains_cache is None:
self.get_grains_centreon(minion_name)
if 'hostgroups' in self.grains_cache:
hostgroups = list(set(self.config['hostgroups'] + self.grains_cache['hostgroups']))
else:
hostgroups = self.config['hostgroups']
return '|'.join(hostgroups)
# Generate the list of hosttemplates for the host to add
def get_hosttemplates(self, minion_name):
if self.grains_cache is None:
self.get_grains_centreon(minion_name)
if 'hosttemplates' in self.grains_cache:
hosttemplates = list(set(self.config['hosttemplates'] + self.grains_cache['hosttemplates']))
else:
hosttemplates = self.config['hosttemplates']
return '|'.join(hosttemplates)
# Function to register the runner on salt-master : test if salt-master configuration is valid
def __virtual__():
try:
Centreon.getConfig()
except Exception as exc:
logger.error(exc)
return False
return True
# The runner action to add host to Centreon Web
def register_instance(minion_name):
try:
# Create the Centreon object
centreon = Centreon()
except Exception as exc:
logger.error(exc)
raise exc
# Test if the host exists in Centreon Web and add it if does not exist
if not centreon.exists(minion_name):
logger.info("Add host %s" % (minion_name))
# Add the host
host.add(
minion_name,
minion_name,
centreon.get_minion_ip(minion_name),
centreon.get_hosttemplates(minion_name),
centreon.config['poller'],
centreon.get_hostgroups(minion_name)
)
# Apply the host templates for create associate services
host.applytpl(minion_name)
# Apply Centreon configuration and reload the engine
poller.applycfg(config['poller'])
Configure the salt-reactor
The salt-reactor is the mechanism which execute an action when an event is fire. See salt documentation for more information.
I will configure the action to add an host when the salt-master receives the event when a salt-minion has started.
In the /etc/salt/master file, I add at the end the configuration for event.
reactor:
- 'salt/minion/*/start':
- /etc/salt/master.d/reactor_monitoring.sls
_salt/minion/*/start_ is the event when a salt-minion start and send this start information to the salt-master.
The /etc/salt/master.d/reactor_monitoring.sls file contains the configuration to call the runner.
minion_to_monitoring:
runner.centreon.register_instance:
- minion_name: {{ data['id'] }}
runner.centreon.register_instance defines the centreon runnner and execute the register_instance action
data[‘id’] is the name of the minion.
After all salt-master configuration, I restart the salt-master service.
service salt-master restart
Configure the salt-minion
This configuration must be done before to start salt-minion, otherwise the host will be added without additional information.
I add some Centreon configuration grains to have a better configuration of my host. I save this configuration into the /etc/salt/minion.d/grains.conf file
The list of configuration information:
| Key name | Description |
|---|---|
| hosttemplates | Additional host templates for the new hosts. |
| hostgroups | Additional host groups to attach the new hosts. |
Example for an host with an http server:
grains:
centreon:
hostgroups:
- frontend
hosttemplates:
- applications-webservers-apache-serverstatus
Example for an host with a MySQL server:
grains:
centreon:
hostgroups:
- backend
hosttemplates:
- applications-databases-
After this configuration, I start the minion service.
service salt-minion start
That’s all 🙂
Do not hesitate to comment and add your improve modification.